Discover the signs, symptoms, and risk factors of hypothyroidism to better understand this common thyroid condition
- What Is Hypothyroidism?
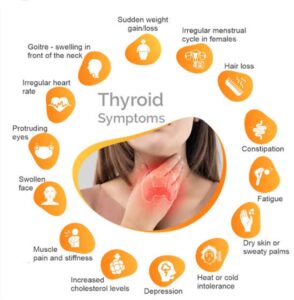
- SYMPTOMS OF HYPOTHYROIDISM
- causes hypothyroidism
- Signs of hypothyroidism.
- TEST TO INCLUDE
- Thy disorders are common, with approximately 12% of individuals experiencing abnormal thyroid function during their lifetime. Women are eight times more likely than to develop thyroid disorder. Furthermore, the likelihood of thyroid increases with age and may present differently in adults compared to children. At its core, thyroid hormone plays a crucial role in regulating energy, growth, and metabolism body. Problems occur when thyroid hormone levels are excessively high or abnormally. Hypothyroidism marked by low levels of thyroid hormone, slows metabolism and hinders the growth and repair of various parts of the body.
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid disease, occurs the thyroid gland fails to produce or release sufficient hormones into the bloodstream in a slowed metabolism. This can lead to unintended weight gain and persistent exhaustion.
While weight gain and fatigue are not exclusive indicators of hypothyroidism, a simple blood test can assist healthcare providers in diagnosing the condition. Fortunately, hypothyroidism is highly treatable. The majority of individuals can effectively manage it through medication and regular follow-up with an Endocrinologist.
However, if left untreated for an extended period, hypothyroidism can become life-threatening. It is to seek evaluation if new symptoms arise.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism symptoms usually develop slowly over time. In some cases, it can take years. Some possible symptoms include:
Brain fog (forgetfulness or difficulty concentrating).
Depression and anxiety.
Dry, coarse skin and hair.
Elevated blood cholesterol levels.
Feeling tired (fatigue).
Frequent or heavy menstrual periods.
Hoarseness.
Inability to tolerate cold temperatures.
Numbness or tingling in your hands.
Physical changes in your face (drooping eyelids, puffiness around your eyes).
Soreness or muscle weakness.
Unexplained weight gain.
What causes hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto’s disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. It’s an autoimmune disease, so it happens when your immune system attacks your thyroid.
hypothyroidism causes include:
-
- Certain medications, including lithium, thalidomide and amiodarone.
- Conditions present at birth, like being born with no thyroid gland or a thyroid gland that doesn’t work properly.
- Iodine deficiency (when you don’t have enough iodine in your body).
- Pituitary gland disorders, including noncancerous tumors.
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid that can happen after a viral illness or pregnancy
-
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- radioactive iodine treatment
- thyroid surgery
- radiation therapy
- medications
- iodine deficiency
Less common causes include:
- pituitary disorders
- congenital disease
- pregnancy
- de Quervain thyroiditis
What are the risk factors for hypothyroidism?
Anyone can get hypothyroidism. But you’re more likely to develop the condition if you’re female or have:
-
- Autoimmune disease.
- Genetic predisposition (a biological parent or sibling with the condition).
- History of thyroid surgery, including thyroid gland removal.
- Pregnancy.
- Previous history of head and neck radiation therapy.
- Started or stopped certain medications.
-
What are the complications of hypothyroidism?
With treatment, hypothyroidism complications aren’t very common. But left untreated, an underactive thyroid can lead to other health conditions like:
- Goiter.
- Heart issues.
- Infertility.
- Miscarriage or birth defects.
- Peripheral neuropathy.
- Myxedema coma (a rare complication that can affect multiple organs and is life-threatening).
-
How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
A healthcare provider will gently examine your thyroid during a physical assessment to check for swelling. They will also inquire about your symptoms and thoroughly review your medical history.
Imaging tests of your thyroid may also be necessary, which could include:
-
-
- Ultrasound.
- Thyroid uptake scan (a type of nuclear medicine imaging).
-
jiliph 17 Jun 2025
JiliPH really stands out with its smooth gameplay and variety of slots like Fortune Gems. For a quick Jili777 Login, check out the app-it’s secure and user-friendly. Great picks for casual and pro players alike! Jili777 Login